游戏资源提取与解压 最终 前文 的逆向结果,与前面三篇文章中的文件提取脚本,重新写一个游戏文件解压脚本。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 import structimport sysimport osfrom multiprocessing import Pooldef hex2short (data ): assert len (data) == 4 return struct.unpack("<i" , data)[0 ] def decompress_chunk (data, size, step ): result = "" j = size / step i = 0 assert step != 0 k = j * step if j > 0 : pos = 0 while True : while pos < k: result += data[pos] pos += j i += 1 if i >= j: break pos = i while k < size: result += data[k] k += 1 return result def decompress_data (data, size, step ): raw_size = size result = "" queue = [ [6 , "\x00" ], [6 , "\x00" ], [6 , "\x00" ], [6 , "\x00" ], [6 , "\x00" ], [6 , "\x00" ], ] def update_queue (lv, ele ): if lv >= 5 : queue[5 ] = queue[4 ] if lv >= 4 : queue[4 ] = queue[3 ] if lv >= 3 : queue[3 ] = queue[2 ] if lv >= 2 : queue[2 ] = queue[1 ] if lv >= 1 : queue[1 ] = queue[0 ] queue[0 ] = ele pos = 8 while size > 0 : instruction = ord (data[pos]) command = instruction >> 5 length = instruction & 0x1F pos += 1 if command == 6 : char = data[pos] update_queue(command, [command, char]) result += char * (length + 2 ) pos += 1 size -= length + 2 elif command == 7 : sub_data = data[pos : pos + length + 1 ] update_queue(command, [command, sub_data]) result += sub_data pos += length + 1 size -= length + 1 else : ref = queue[command] update_queue(command, ref) if ref[0 ] == 6 : result += ref[1 ] * (length + 2 ) size -= length + 2 elif ref[0 ] == 7 : dp = length >> 2 dl = length & 3 result += ref[1 ][dp : dp + dl + 1 ] size -= dl + 1 else : return decompress_chunk(result, raw_size, step) return decompress_chunk(result, raw_size, step) def decompress (i, data, file_size, output_dir, compressed, is_voice, is_sound ): if data and compressed: data = decompress_data( data, size=hex2short(data[:4 ]), step=hex2short(data[4 :8 ]) ) if data[:4 ] == "TIM2" : filename = os.path.join(output_dir, "%05d.tm2" % i) elif data[:2 ] == "BM" : filename = os.path.join(output_dir, "%05d.bmp" % i) elif data[0 :1 ] == "[" : filename = os.path.join(output_dir, "%05d.lst" % i) elif len (data) > 4 and hex2short(data[:4 ]) == 0x4952FAFA : filename = os.path.join(output_dir, "%05d.cnut" % i) else : filename = os.path.join(output_dir, "%05d.dat" % i) with open (filename, "wb" ) as f: if is_voice or is_sound: data = ( b"\x56\x41\x47\x70" + b"\x00\x00\x00\x06" + b"\x00\x00\x00\x00" + struct.pack(">I" , file_size) + b"\x00\x00\x56\x22" + b"\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00" + ("%s" % i).encode().ljust(16 , b"\x00" ) + data ) f.write(data) if is_voice or is_sound: tmp_name = filename filename = os.path.join(output_dir, "%05d.wav" % i) os.system("ffmpeg -i '%s' '%s'" % (tmp_name, filename)) os.remove(tmp_name) print (" Extracted: %s" % filename) def main (hd_filename ): if not os.path.exists(hd_filename): print ("%s does not exists." % hd_filename) return pool = Pool(6 ) prefix = "." .join(hd_filename.split("." )[0 :-1 ]) compressed = ( prefix.endswith("NORMAL" ) or prefix.endswith("SCENE_ID" ) or prefix.endswith("SCENEDAT" ) ) is_voice = prefix.endswith("VOICE_ID" ) is_sound = prefix.endswith("SOUND_ID" ) output_dir = prefix if not os.path.exists(output_dir): os.mkdir(output_dir) print ('Extracting "%s" to "%s"...' % (prefix, output_dir)) head_filename = prefix + ".HD" head_size = os.path.getsize(head_filename) head_file = open (head_filename, "rb" ) bin_filename = prefix + ".BIN" bin_size = os.path.getsize(bin_filename) bin_file = open (bin_filename, "rb" ) if head_size % 4 != 0 : print (" Invalid head file size: " + hex (head_size)) head_file.close() bin_file.close() return print (" Head file size: " + hex (head_size)) print (" Bin file size: " + hex (bin_size)) file_count = head_size >> 2 print (" Total %d files to be extracted." % file_count) for i in range (file_count): file_size = hex2short(head_file.read(4 )) data = "" if file_size: data = bin_file.read(file_size) j = 1 while True : if j * 0x800 >= bin_file.tell(): s = bin_file.read(j * 0x800 - bin_file.tell()) assert len (s.replace(b"\xff" , b"" )) == 0 break j += 1 pool.apply_async( decompress, args=(i, data, file_size, output_dir, compressed, is_voice, is_sound), ) pool.close() pool.join() head_file.close() bin_file.close() if __name__ == "__main__" : main(sys.argv[1 ])
extract_hd_bin.py 结合了前面三篇文章中所有的提取与转换脚本,仅需要提供 .HD 文件的路径就可以自动提取、解压、识别、转换文件。
仅在 python2 下运行,支持多进程(6 进程,可修改),例如 python2 extract_hd_bin.py ./xxxxx/NORMAL.HD,该脚本会自动将 ./xxxxx/NORMAL.BIN 的文件提取至 /xxxxx/NORMAL/ 目录下,以文件出现顺序作为文件名,例如 00000.dat。
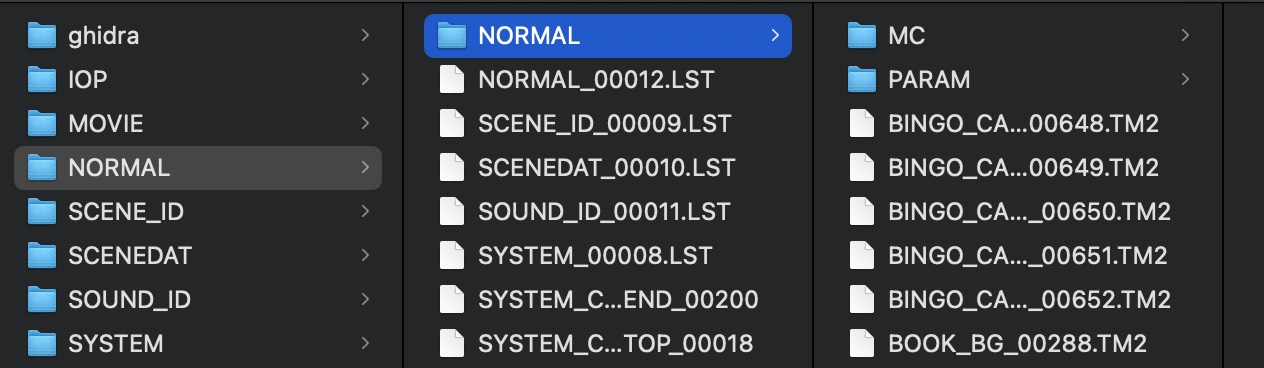
通过分析可以发现,仅 NORMAL、 SCENE_ID 和 SCENE_DAT 中的文件被压缩,其余 3 个 .BIN 未被压缩,SOUND_ID、VOICE_ID 中仍然保存的音频 ADPCM 裸数据,SYSTEM 中保存明文。
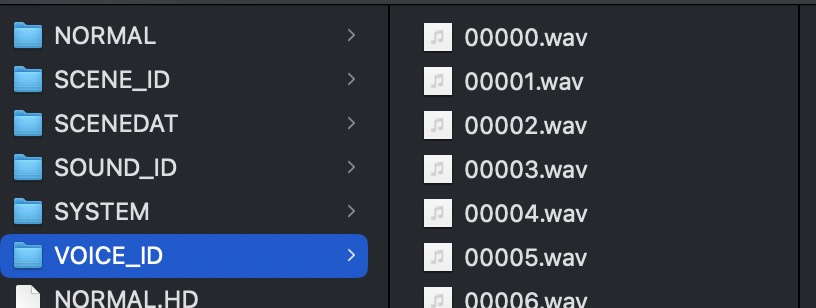
脚本支持识别 .cnut、.bmp 以及 .tm2 文件,未被识别出的文件类型以 .dat 结尾。识别出的 ADPCM 将自动拼接 VAG 文件头并且用 ffmpeg 转换为 wav 文件,需要命令行存在 ffmpeg 命令。
对于 .tm2 图片文件,推荐使用 XnConvert 批量转换为 PNG 文件。
文件名称与路径恢复 基于 NORMAL 中提取的几个 LST 文件,使用如下脚本可以将 extract_hd_bin.py 提取出的文件恢复到 LST 中指定的文件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 import osimport reimport sysdef main (directory, name_list_file ): name_list = list () with open (name_list_file, "rt" ) as f: for line in f.readlines(): line = line.strip() if len (line) == 0 or line[0 ] == "[" or line.startswith("//" ): continue name_list.append(os.path.join(directory, line.replace("\\" , "/" ))) src_files = [ os.path.join(directory, i) for i in sorted (os.listdir(directory)) if re.match (r"^\d+\.[a-zA-Z0-9]+$" , i) ] assert len (src_files) == len (name_list), "%d != %d" % ( len (src_files), len (name_list), ) for i in range (len (src_files)): src_file = src_files[i] no = os.path.basename(src_file).split("." )[0 ] dst_file = name_list[i] if "." in os.path.basename(dst_file): dst_file = dst_file.split("." ) if dst_file[-1 ] in ("NUT" , "nut" ): with open (src_file, "rb" ) as f: if f.read(2 ) == "\xfa\xfa" : dst_file[-1 ] = "cnut" dst_file = "." .join(dst_file[:-1 ]) + "_" + no + "." + dst_file[-1 ] else : dst_file += "_" + no dst_dir = os.path.dirname(dst_file) if not os.path.exists(dst_dir): os.makedirs(dst_dir) print ("Rename %s -> %s" % (src_file, dst_file)) os.rename(src_file, dst_file) if __name__ == "__main__" : main(sys.argv[1 ], sys.argv[2 ])
仅在 Python2 下运行,例如 python2 rename.py ./xxxx/NORMAL/ ./xxxx/NORMAL/00011.lst 可以恢复已经解压出的 NORMAL 文件名,并且文件名中携带文件原本的编号便于 debug。
注意恢复完 NORMAL 后,如果接着恢复其他文件,则需要指定 NORMAL 中已经恢复的 LST 文件名,而不是文件编号。
Squirrel 字节码反编译 以下脚本完善了 前文 中反编译 cnut 字节码的流程,可自动处理反编译后脚本中的 shift-jis 编码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 import osimport subprocessimport sysdef text2shift_jis (data ): result = '' i = 0 length = len (data) while i < length: c = data[i] if c == '"' : j = i + 1 string = "" while data[j] != '"' : string += data[j] j += 1 if '\\x00' in string: string = eval ('b"' + string.replace('\\x00' , '\\x' ) + '"' ) string = string.decode('shift-jis' ) string = string.replace('\r' ,'\\r' ).replace('\n' , '\\n' ) result += '"' + string + '"' i = j else : result += c i += 1 return result.encode('shift-jis' ) def main (directory ): for root, directories, files in os.walk(directory): for filename in files: code = None if filename.endswith('.cnut' ) and os.path.exists('./nutcracker.exe' ): filename = os.path.join(root, filename) print ('Decompiling %s...' % filename) code = subprocess.check_output(['./nutcracker.exe' , filename]) elif filename.endswith('.nut' ) or filename.endswith('.NUT' ): filename = os.path.join(root, filename) with open (filename, 'rb' ) as f: code = f.read() if code is not None : if '\\x00' in code: print ('Translating %s...' % filename) code = text2shift_jis(code) with open (filename.replace('.cnut' , '.nut' ), 'wb' ) as f: f.write(code) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv[1 ])
仅在 Python2 与 Windows 下运行,同目录下需要存在 nutcraker.exe。例如 python2 decompile_cnut.py ./xxxx/SYSTEM/ 可以自动反编译 ./xxxx/SYSTEM/ 下所有的 .cnut 文件,并且对于所有的 .nut 文件自动处理 shift-jis 编码字符串。
目标数据提取 至此,针对这个 PS2 游戏已经破解的差不多了,所有文件都解压完成,总结一下每个 .BIN 文件都是做什么的:
NOTMAL.BIN:主要包含了程序中的一些界面图片,以及其他几个文件的解压后目录结构与文件名,还包含了字库图片。
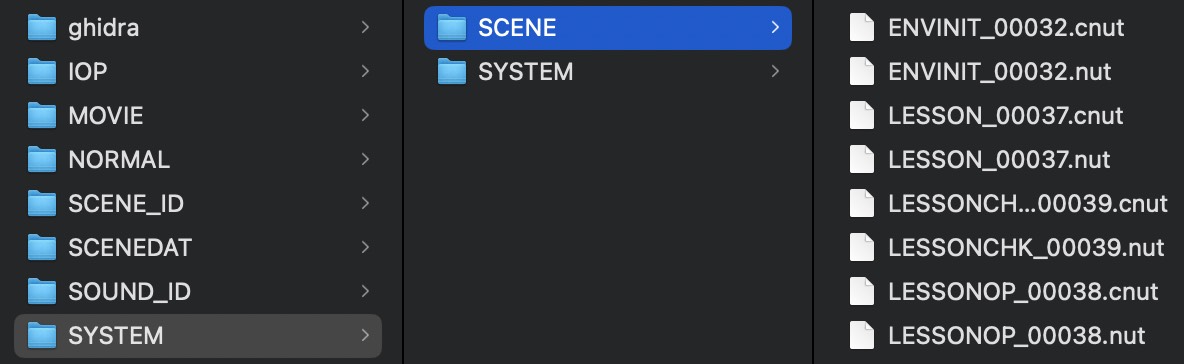
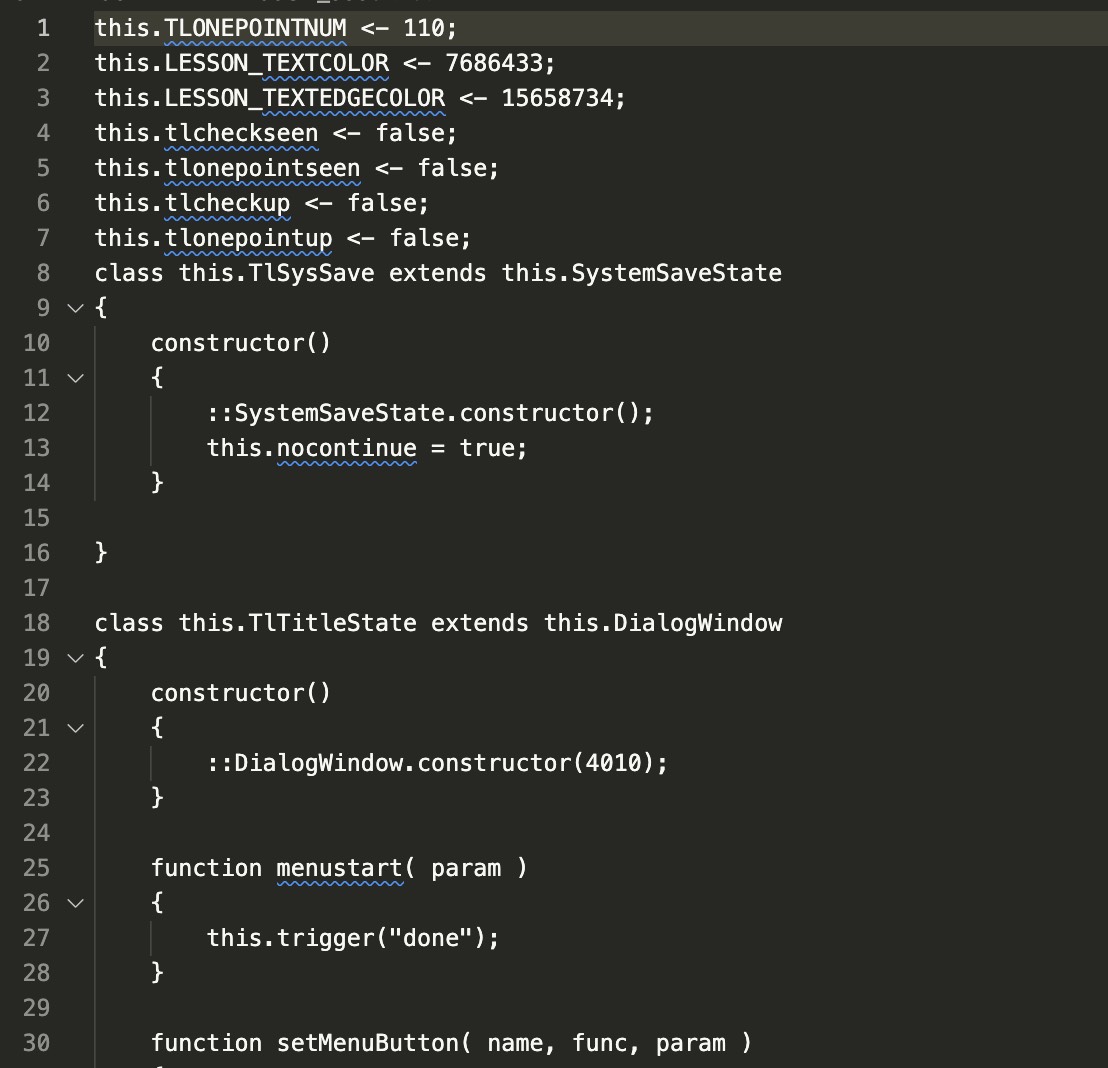
SYSTEM.BIN:包含了 Squirrel 脚本的主逻辑。一半 .cnut 字节码文件,一半 .nut 明文文件。推测经常被调用的函数被封装到 .cnut 中。
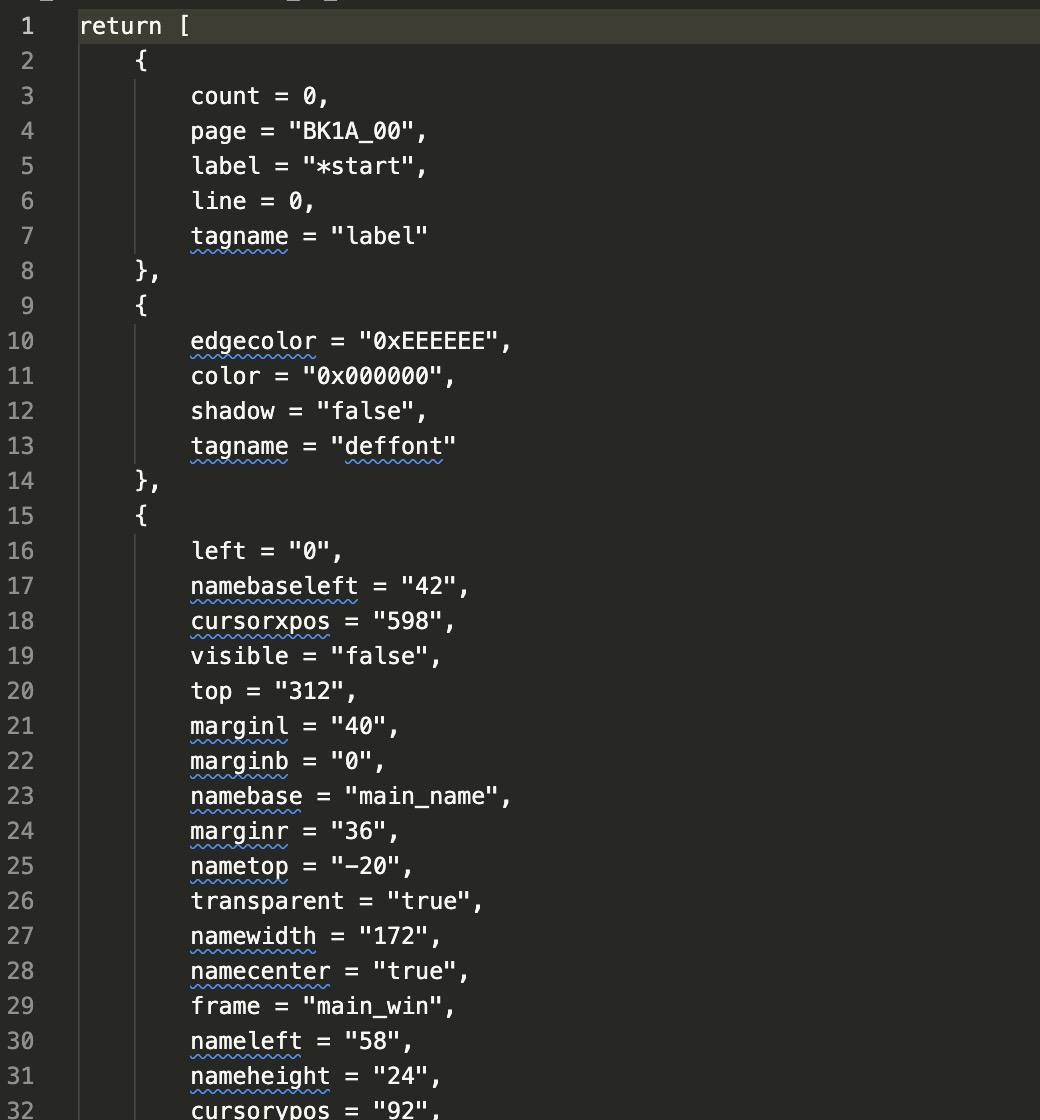
SCENE_ID.BIN:全部都是 .cnut,一个文件代表一个游戏场景的流程,反编译后每一个 .nut 中都是一个数组,数组中每一个对象都代表一个游戏动作。推测 SYSTEM 主要通过游戏主程序调用 SYSTEM_ID 中的场景。
SCENEDAT.BIN:全部都是 .tm2 图片,游戏中所有任务、场景、贴图资源,
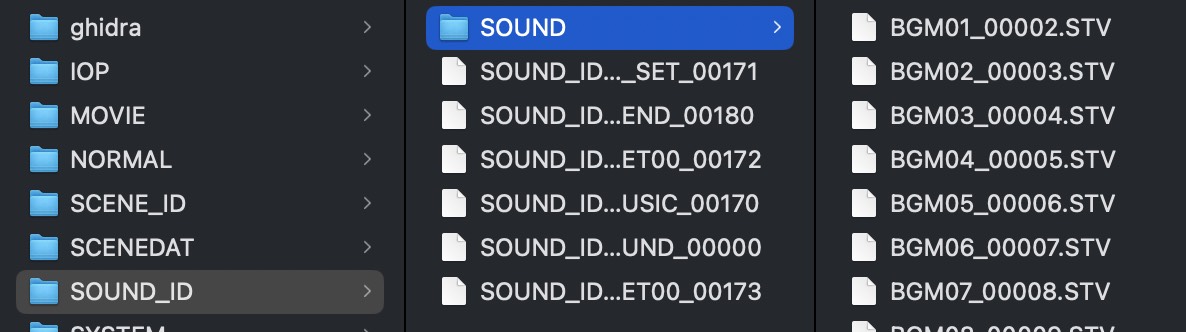
SOUND_ID.BIN:游戏中的音效、BGM 等(.STV 文件),部分非音频文件作用未知。
VOICE_ID.BIN:游戏中所有任务的语音音频。
我们的最终目标是提取出每个角色说的语音音频以及对应的台词,这些数据主要放在 SCENE_ID 中,分析反编译后的 .nut 可以发现,该目录下所有脚本都返回了一个列表,结合 前文 中对 SYSTEM 的初步分析,每个脚本文件都是一个场景下的顺序序列,这个列表中每一个元素都是一个动作,首先来分析一下那些动作是让角色说话。
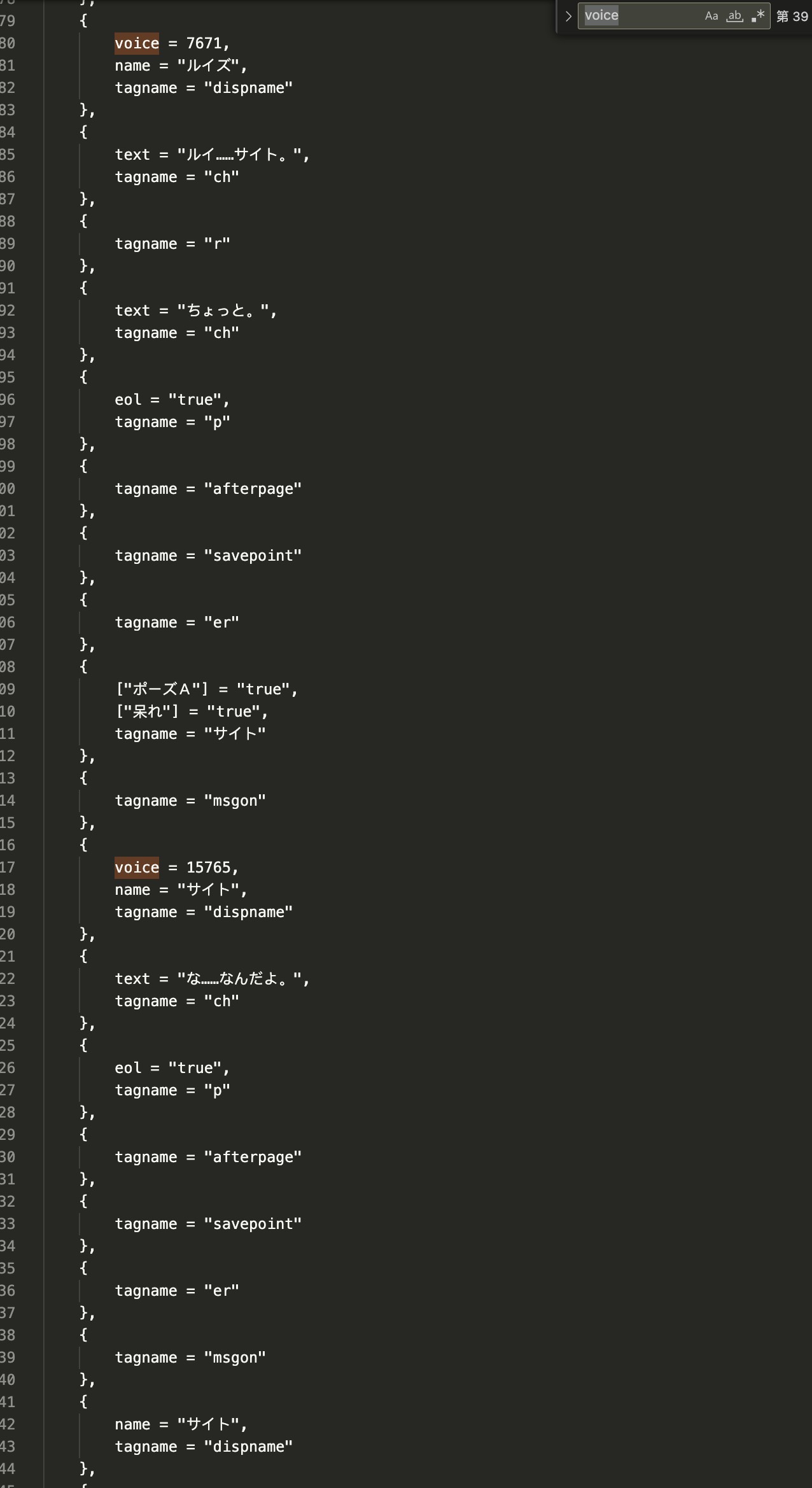
直接搜索 voice,可以看到每一个 voice 后面都跟着一个数字,推测该数字就是 VOICE_ID 中文件的序号。从 前面 的分析可以得知,当 tagname 为 ch 的时候就是打印在屏幕上的台词。
那么可以找到规律:在一个场景中,如果与奥 tagname 是 dipname 时,播放 VOICE_ID 中对应的音频,并且说话者就是 name,在之后的动作中如果 tagname 是 ch,那么就对应了上一个遇到的 voice 对应的台词,ch 可多次出现,知道遇到 tagname 为 p 的时候停止。
此外,推测 tagname 为 afterpage 的时候代表对话框翻页,sagepoint 代表自动保存,msgon 和 msgoff 代表显示、关闭对话框。
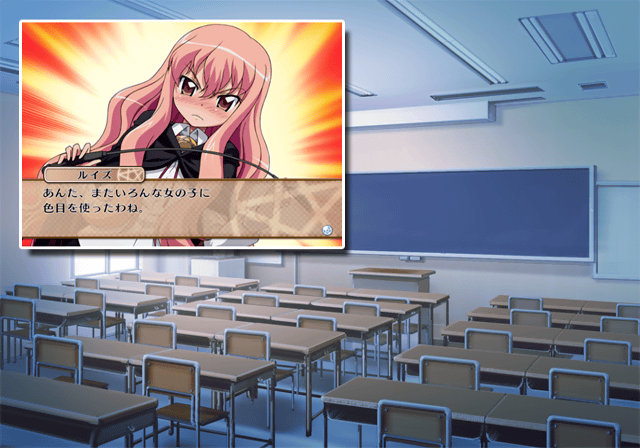
验证一下上图中 15765 号音频与对应的台词是否对的上。
基于此,可以写一个对应的音频和台词提取脚本:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 import osimport jsonimport sysdef save_data (scenes, voices, directory ): output_directory = os.path.join(directory, ".." , "voice_data" ) if not os.path.exists(output_directory): os.mkdir(output_directory) output_scenes_name = os.path.join( output_directory, os.path.basename(directory.replace("\\" , "/" ).rstrip("/" )) + ".json" , ) output_voices_name = os.path.join( output_directory, os.path.basename(directory.replace("\\" , "/" ).rstrip("/" )) + ".voices.json" , ) with open (output_scenes_name, "wt" ) as f: f.write(json.dumps(scenes, indent=4 , ensure_ascii=False ).encode("utf-8" )) with open (output_voices_name, "wt" ) as f: f.write(json.dumps(voices, indent=4 , ensure_ascii=False ).encode("utf-8" )) voice_dir = os.path.join(directory, ".." , "VOICE_ID" ) for name, voice in voices.items(): name_dir = os.path.join(output_directory, name) if not os.path.exists(name_dir): os.mkdir(name_dir) wav_dir = os.path.join(name_dir, "wavs" ) if not os.path.exists(wav_dir): os.mkdir(wav_dir) meta_file = os.path.join(name_dir, "metadata.csv" ) with open (meta_file, "wb" ) as f: for voice_id, sentence in voice: wav_filename = b"%05d.wav" % voice_id print ( "cp %s -> %s" % ( os.path.join(voice_dir, wav_filename), os.path.join(wav_dir, wav_filename), ) ) with open (os.path.join(voice_dir, wav_filename), "rb" ) as g, open ( os.path.join(wav_dir, wav_filename), "wb" ) as h: h.write(g.read()) f.write(wav_filename + b"|" + sentence.encode("utf-8" ) + b"\n" ) def main (directory ): scenes = {} voices = {} for root, directories, files in os.walk(directory): for filename in files: if filename.endswith(".nut" ) or filename.endswith(".NUT" ): basename = "." .join(filename.split("." )[:-1 ]) filename = os.path.join(root, filename) print ("Loading %s..." % filename) with open (filename, "rb" ) as f: code = f.read().strip().decode("shift-jis" ) if code.startswith("return [" ): print (" Found scene at %s" % filename) code = "\n" .join( ( i.replace('\t\t["' , "\t\t" , 1 ) .replace('"] = ' , " = " , 1 ) .replace(" = " , '": ' , 1 ) .replace("\t\t" , '\t\t"' , 1 ) for i in code.split("\n" ) ) ) scene = json.loads(code[7 :].rstrip(";" )) scenes[basename] = scene sentence = voice_id = voice_name = None start = False for ele in scene: if "voice" in ele: assert ele["tagname" ] in ("dispname" , "entryvoice" ), ele[ "tagname" ] if start is True : print ("Already started!" , voice_id) voice_id = ele["voice" ] voice_name = ele["name" ] sentence = "" start = True elif start: if ele.get("tagname" , None ) == "p" : start = False if sentence is not None : if voice_name not in voices: voices[voice_name] = list () voices[voice_name].append((voice_id, sentence)) elif ele.get("tagname" , None ) == "ch" and "text" in ele: sentence += ele["text" ] elif "\ntalk(" in code: print (" Found scene at %s" % filename) scene = code.split("\n" ) scenes[basename] = scene for line in scene: line = line.encode("shift-jis" ) if line.startswith("talk" ): line = eval ( line[4 :] .rstrip(";" ) .replace("null" , "None" ) .replace("\\n" , "" ) .replace("0x04000000" , "" ) ) voice_name = line[0 ] voice_id = line[-1 ] sentence = line[-2 ] if line[-1 ] is not None : voice_name = voice_name.decode("shift-jis" ) sentence = sentence.decode("shift-jis" ) if voice_name not in voices: voices[voice_name] = list () voices[voice_name].append((voice_id, sentence)) save_data(scenes, voices, directory) if __name__ == "__main__" : main(sys.argv[1 ])
该脚本仅在 Python2 下运行,例如 python2 load_scene.py ./xxxx/SCENE_ID/ 将自动根据 ./xxxx/SCENE_ID/ 中的每一个脚本从 ./xxxx/VOICE_ID/ 中提取对应的音频以及台词.
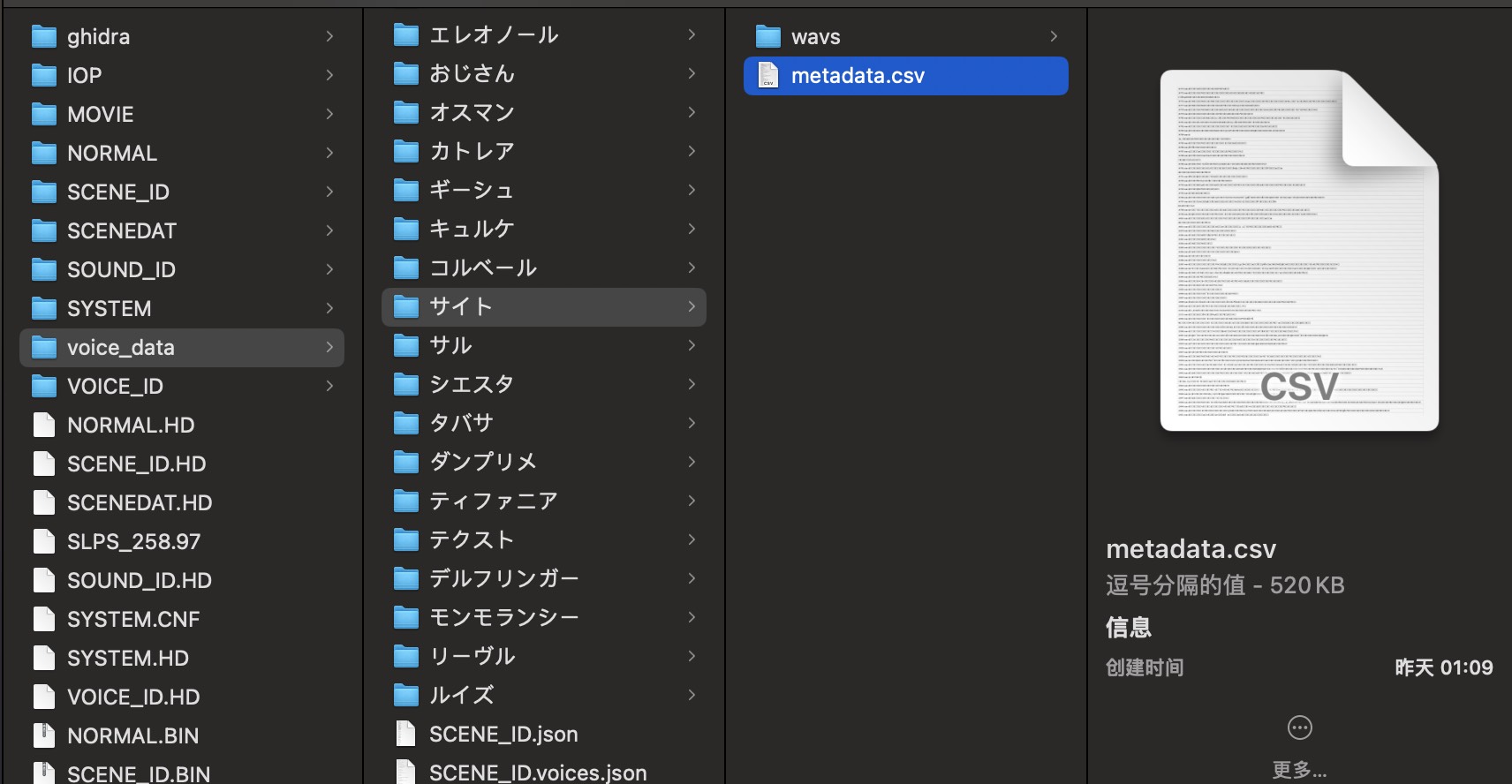
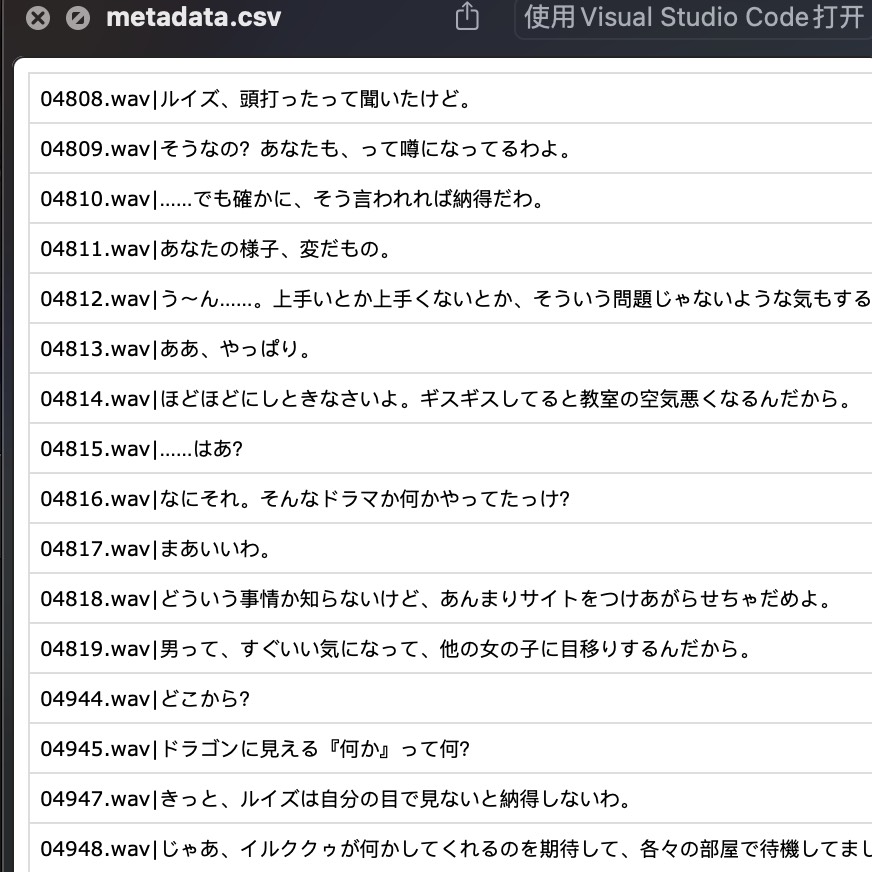
同时会在 ./xxxx/voice_data/ 根据每个角色新建目录,目录中保存了 metadata.csv 以及包含了该角色所有语音的 wavs 目录。
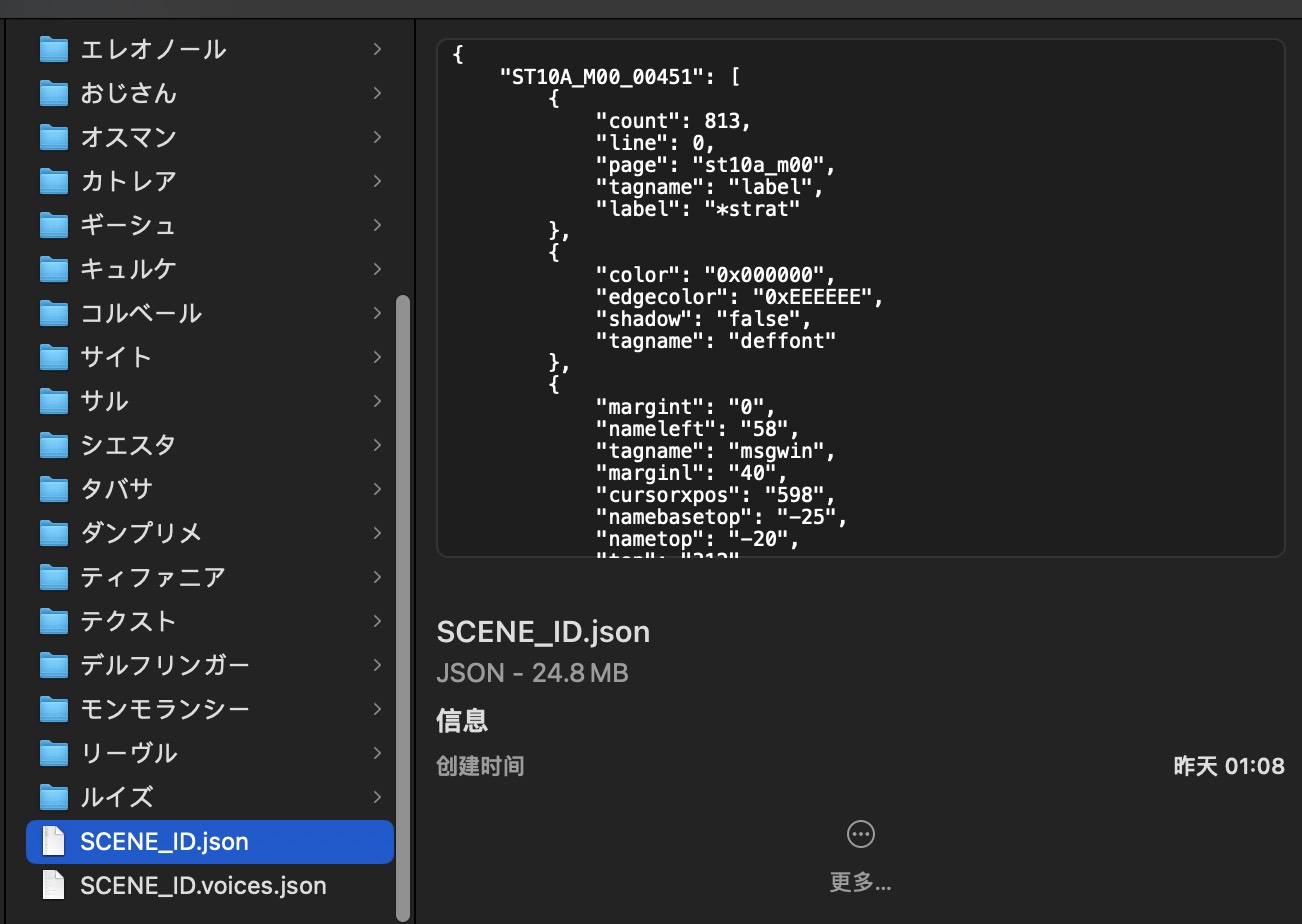
此外还会将游戏所有场景数据保存在一个 ./xxxx/voice_data/SCENE_ID.json 中,
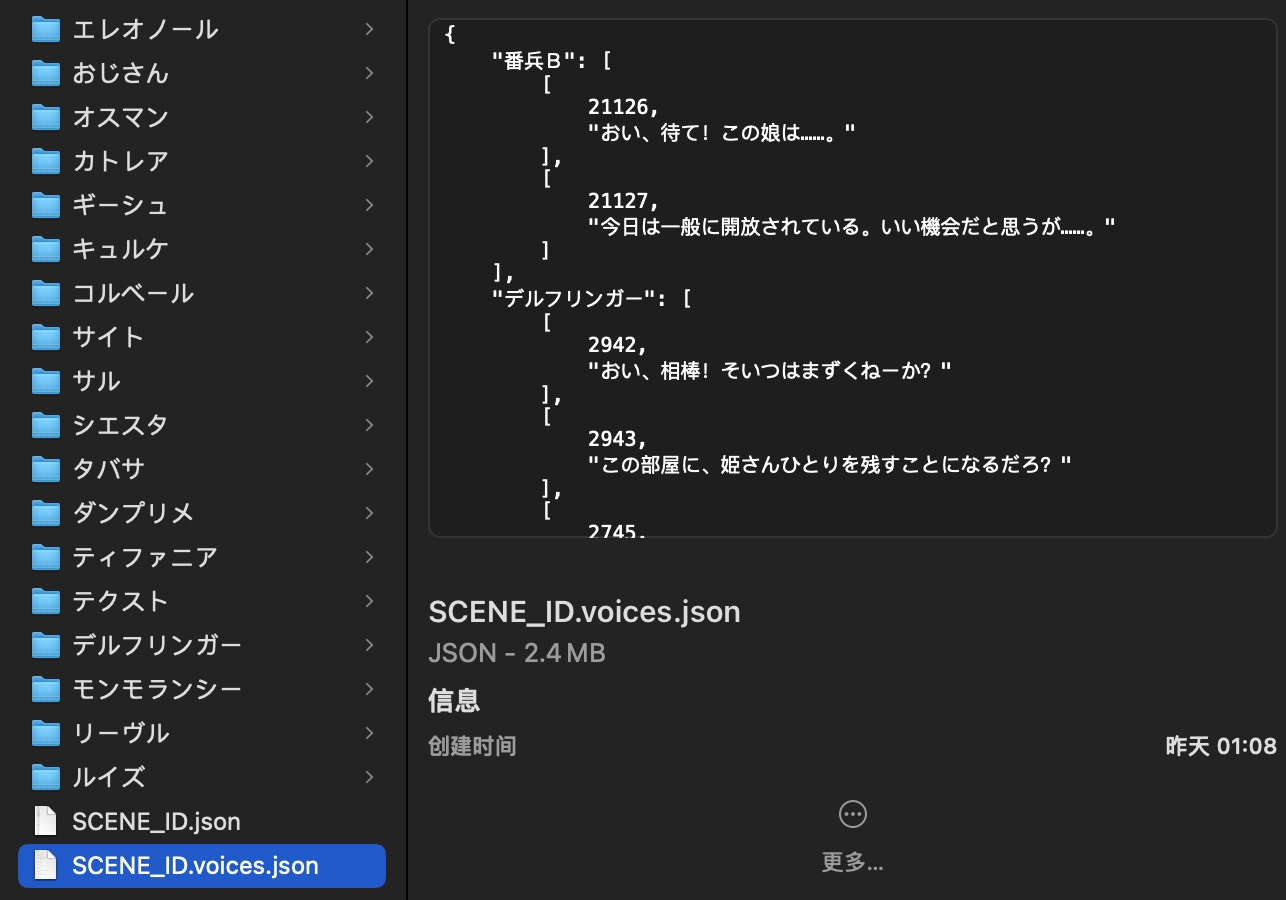
以及将所有场景下的音频文件 ID 与台词数据保存在 ./xxxx/voice_data/SCENE_ID.voices.json 中,便于 debug。
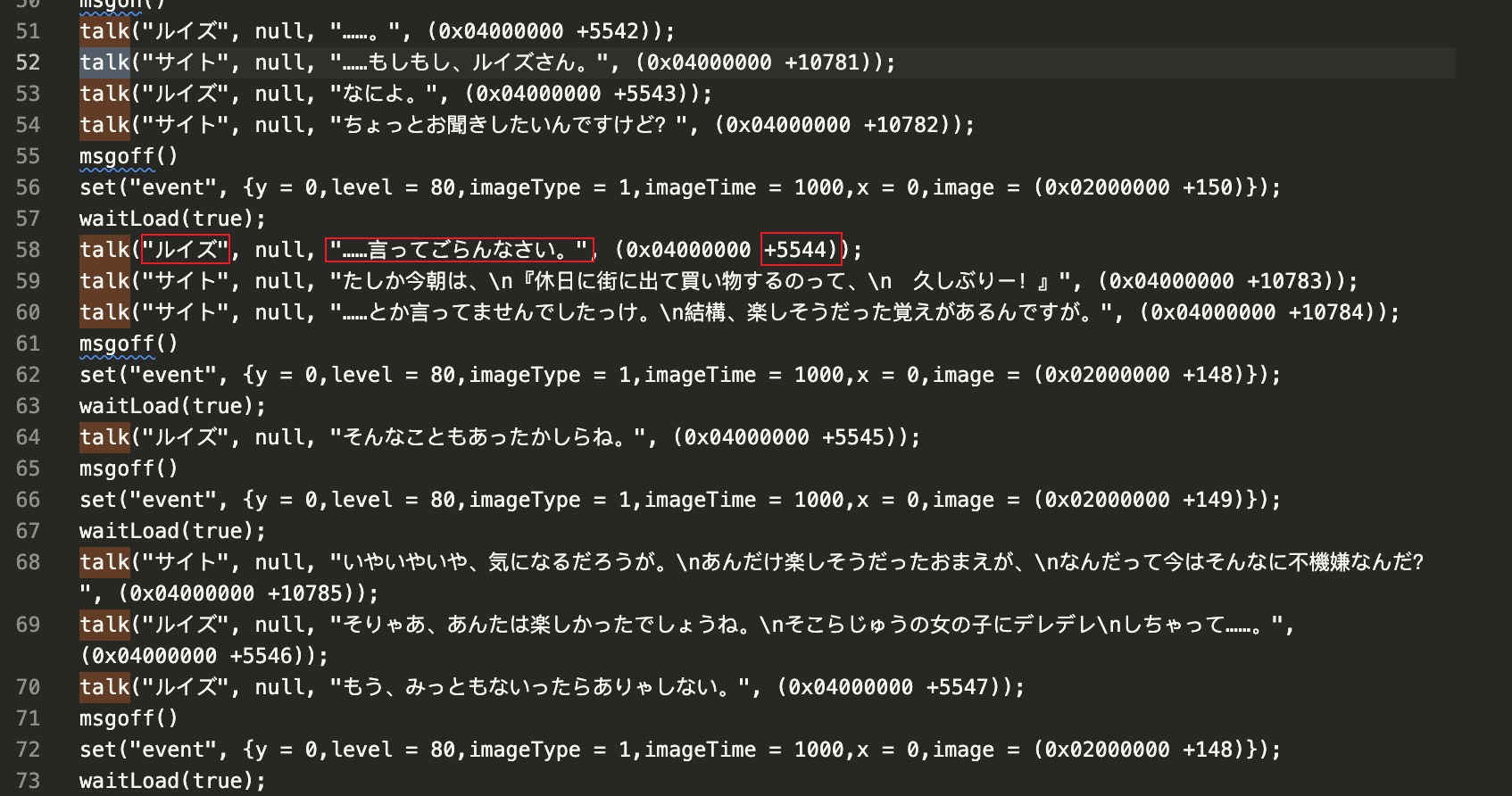
该脚本还兼容了此游戏系列的另一款同类游戏的 SCENE_ID 格式,例如:
直接调用了 talk 函数使角色说话,从左至右依次是说话人、未知、台词、以及程序基址 + 音频 ID。
最终的 voice_data 里就是我们的提取的目标 metadata.csv 以及 `wavs。